Diagnosing and Care for Diabetic Retinopathy
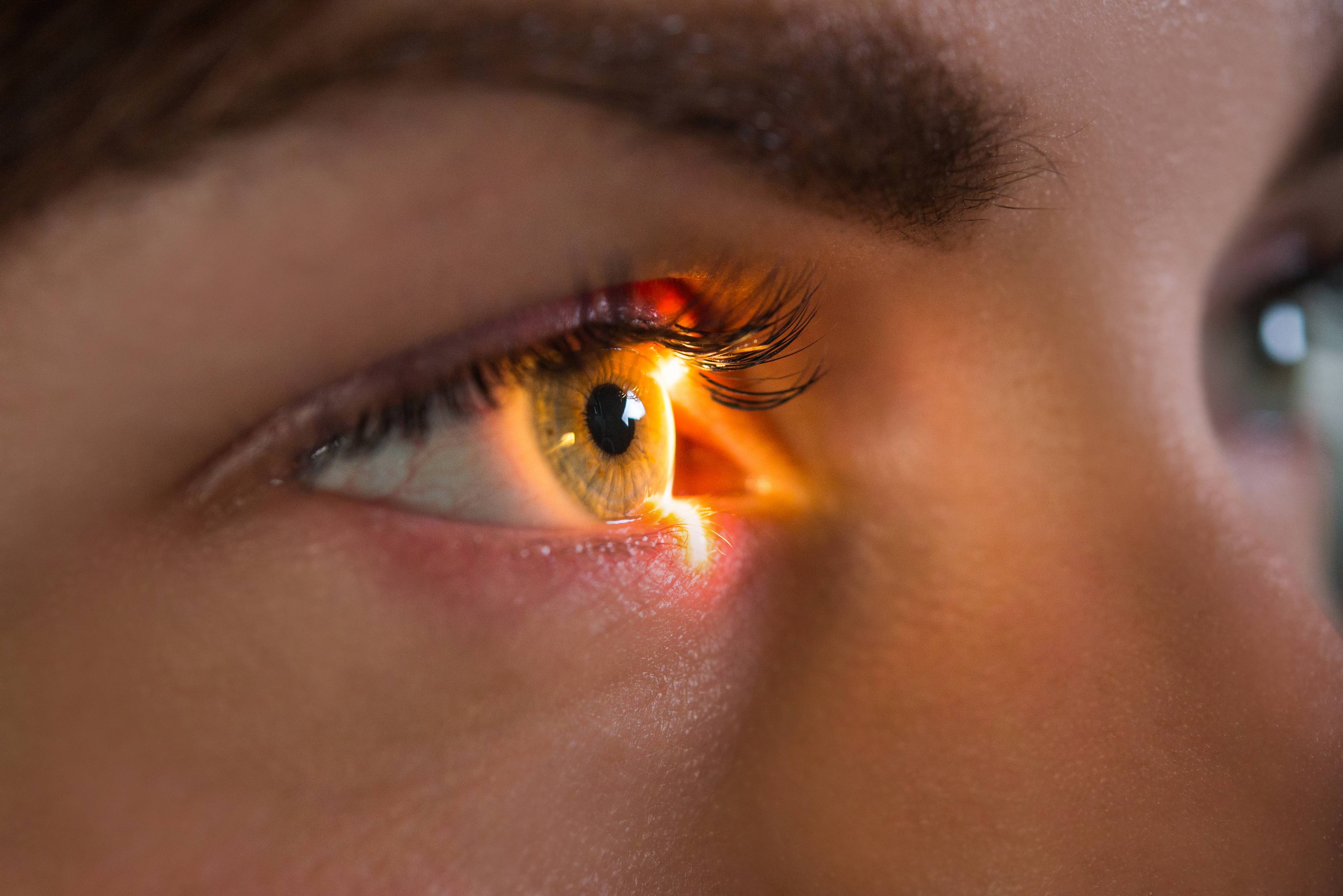
If you are diabetic, work with your physician to control your blood sugar. Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can lead to blindness in people living with diabetes. High levels of blood sugar injure blood vessels inside the retina and cause vision loss.
More than 2 in 5 Americans with diabetes have diabetic retinopathy. Also, people with diabetes are at higher risk of getting other vision problems, including glaucoma and cataracts. Diabetic retinopathy affects both eyes, and the complication does not have any early warning signs.
Diagnosing Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy usually begins without any noticeable changes in eyesight. However, your eye doctor or ophthalmologist can detect signs of the condition through an eye exam. The following procedures are used to diagnose diabetic retinopathy.
Dilated Eye Examination
During a dilated eye exam, your doctor will put drops in your eyes. These drops will dilate your pupils and enable your doctor to look inside your eyes. Your doctor will then take photos of the inner parts of your eyes to look for:
Irregularities in the retina, blood vessels, or optic nerve
Variations in eye pressure
Cataracts
Scarring
Retinal detachment
Abnormal blood vessels
Fluorescein Angiography
With your pupils dilated, your doctor will take pictures of your retina to assess its health. To get clear signs, your doctor will inject a yellow dye into a vein in your arm and take pictures as the dye is moving through your blood vessels. This examination will reveal whether any blood vessels are leaky or blocked. The test will also detect other irregularities in the blood vessels.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT is another method used to examine your retina. A non-invasive device scans your eyes and produces detailed photos of your retina’s thickness. This helps your ophthalmologist detect and measure inflammation inside your retina. Your doctor can also take OCT scans to see how well a treatment is working.
Care for Diabetic Retinopathy
How to care for diabetic retinopathy depends on various factors, including the severity of the complication and how it has responded to previous treatments. At first, your doctor may choose to observe your eyes without meddling with them. In some cases, you may need a thorough dilated eye examination every 2 to 4 months while you work on regulating your blood sugar.
Options for treatment may include:
Laser Surgery
Your doctor may use laser treatment to treat leaky blood vessels and reduce inflammation of your retina. Laser treatment can also shrink abnormal blood vessels and stop them from budding again. Sometimes you may need more than one laser surgery.
Injections
Your doctor may give you certain injections and eye medications to relieve swelling and prevent blood vessels from leaking into your eye.
Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy surgery may be necessary to empty fluid and blood from leaky vessels in your retina. This will allow your retina to regain its ability to focus light properly. The surgery might also remove scarring from your retina.
Learn more about diagnosing & care for diabetic retinopathy, visit St. Marys Family Eye Care in St. Marys, OH at 419-800-0400 to book an appointment.






